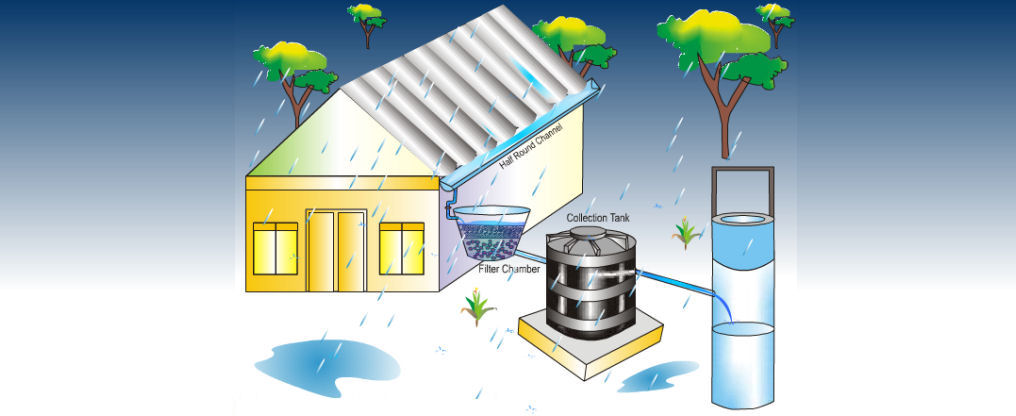
Storage of Direct Use
In this method rain water collected from the roof of the building is diverted to a storage tank. The storage tank has to be designed according to the water requirements, rainfall and catchment availability. Each drainpipe should have mesh filter at mouth and first flush device followed by filtration system before connecting to the storage tank. It is advisable that each tank should have excess water over flow system.
Excess water could be diverted to recharge system. Water from storage tank can be used for secondary purposes such as washing and gardening etc. This is the most cost effective way of rainwater harvesting. The main advantage of collecting and using the rainwater during rainy season is not only to save water from conventional sources, but also to save energy incurred on transportation and distribution of water at the doorstep. This also conserves groundwater, if it is being extracted to meet the demand when rains are on. A typical storage tank is shown on the right
Recharging ground water aquifers
Ground water aquifers can be recharged by various kinds of structures to ensure percolation of rainwater in the ground instead of draining away from the surface. Commonly used recharging methods are listed below,
Recharging of bore wells
Rainwater collected from rooftop of the building is diverted through drainpipes to settlement or filtration tank. After settlement filtered water is diverted to bore wells to recharge deep aquifers. Abandoned bore wells can also be used for recharge. Optimum capacity of settlement tank/filtration tank can be designed on the basis of area of catchement, intensity of rainfall and recharge rate. While recharging, entry of floating matter and silt should be restricted because it may clog the recharge structure. First one or two shower should be flushed out through rain separator to avoid contamination.
Recharge Pits
Recharge pits are small pits of any shape rectangular, square or circular, contracted with brick or stone masonry wall with weep hole at regular intervals. Top of pit can be covered with perforated covers. Bottom of pit should be filled with filter media. The capacity of the pit can be designed on the basis of catchment area, rainfall intensity and recharge rate of soil. Usually the dimensions of the pit may be of 1 to 2 m width and 2 to 3 m deep depending on the depth of pervious strata. These pits are suitable for recharging of shallow aquifers, and small houses.
Soak way or Recharge shafts
Soak away or recharge shafts are provided where upper layer of soil is alluvial or less pervious. These are bored hole of 30 cm dia. up to 10 to 15 m deep, depending on depth of pervious layer. Bore should be lined with slotted/perforated PVC/MS pipe to prevent collapse of the vertical sides. At the top of soak away required size sump is constructed to retain runoff before the filters through soak away. Sump should be filled with filter media.
Recharge Trenches
Recharge trench in provided where upper impervious layer of soil is shallow. It is a trench excavated on the ground and refilled with porous media like pebbles, boulder or brickbats. it is usually made for harvesting the surface runoff. Bore wells can also be provided inside the trench as recharge shafts to enhance percolation. The length of the trench is decided as per the amount of runoff expected. This method is suitable for small houses, playgrounds, parks and roadside drains. The recharge trench can be of size 0.50 to 1.0 m wide and 1.0 to 1.5 m deep.
Percolation tank
Percolation tanks are artificially created surface water bodies, submerging a land area with adequate permeability to facilitate sufficient percolation to recharge the ground water. These can be built in big campuses where land is available and topography is suitable. Surface run-off and roof top water can be diverted to this tank. Water accumulating in the tank percolates in the solid to augment the ground water. The stored water can be used directly for gardening and raw use. Percolation tanks should be built in gardens, open spaces and roadside green belts of urban area.